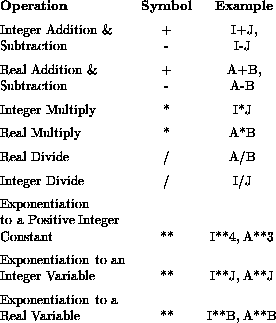
Every operation on a computer has an associated cost. As users, the game we must play is to complete the task in hand whilst minimising the overall cost. The following table gives a very rough guide to the cost of certain operations:

On some machines floating point arithmetic will be quicker than the equivalent integer arithmetic. This is especially true if the machine has a dedicated floating point processor (a maths co-processor.) In general divisions are much slower than multiplications (by a factor of 5 or more). The speed of calculation of exponentiated numbers depends on the exponent and to a certain extent the base. Some REAL exponents, such as the literal 0.5 (square root) are very quick as a special purpose algorithm can be called (SQRT).
Return to corresponding overview page ![]()